Cloud migration is no longer optional—it’s essential for businesses aiming to grow fast and stay flexible. Moving your apps and data to the cloud means better scalability, security, and cost savings.
But the process can feel tricky without the right plan. Knowing the best strategies and tools helps you avoid headaches and get the most from your cloud move.
Whether you’re just starting or updating your IT, understanding cloud migration in 2025 is key to staying competitive and agile.
This blog provides comprehensive insights on these subjects to help you with your cloud migration plan. Let’s break it down!
Introduction to Cloud Migration
Cloud computing provides businesses with the tools, storage, security, software, and services they require to achieve their goals. Many businesses decide to move their databases, apps, and core systems to the cloud to take advantage of these benefits.
When you migrate to the cloud, these workloads are moved from on-premises data centers to the cloud provider’s infrastructure in a planned, non disruptive manner. Businesses that use the cloud are said to save 20% on infrastructure.
To move your operations to the cloud in an organized manner, you must plan, test, and prioritize your workloads using a cloud migration strategy.
Different Types of Cloud Migration
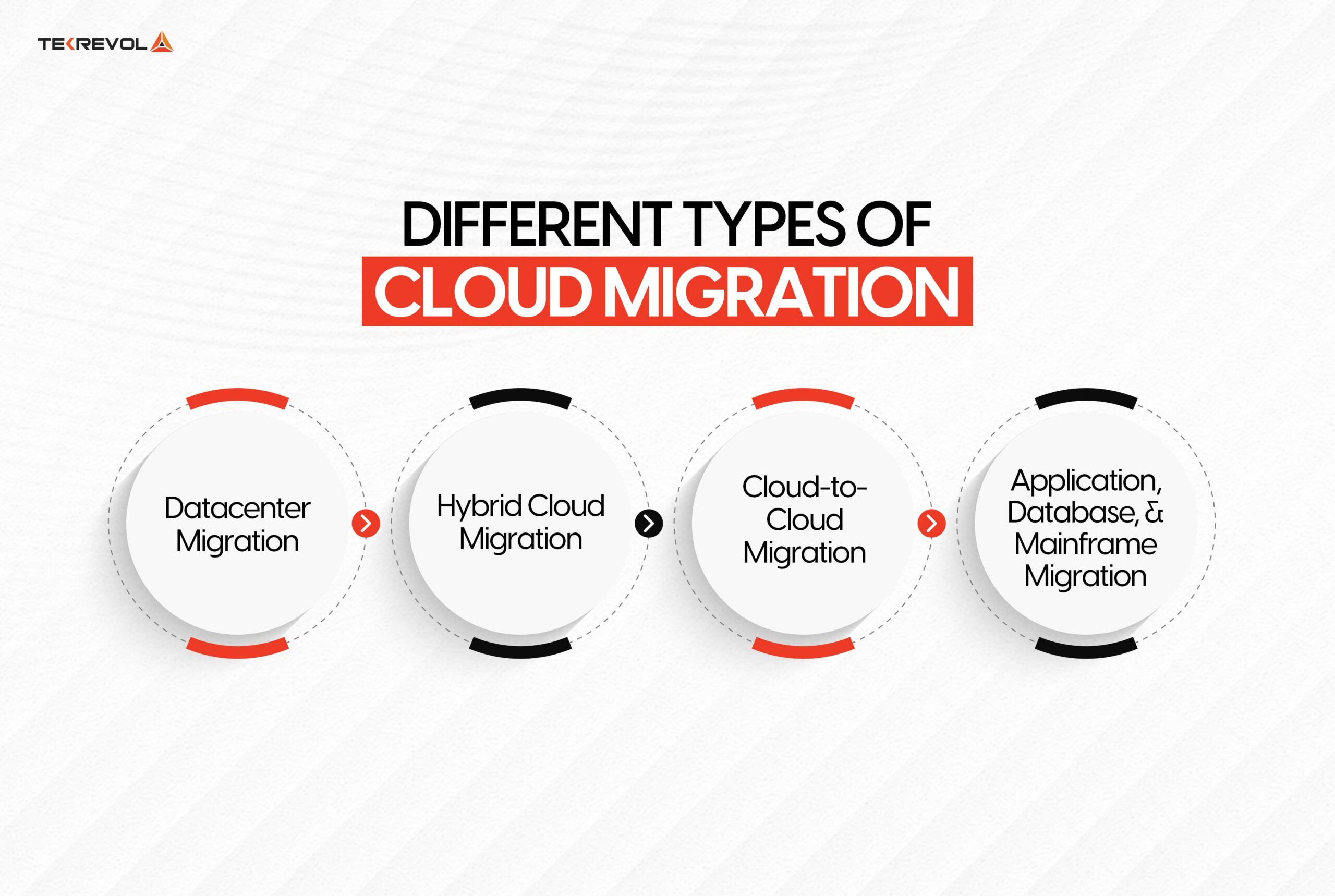
There are several types of migration, and each is designed to meet certain technological requirements as well as commercial demands.
Understanding these categories helps businesses in selecting the ideal approach for moving their digital assets to the cloud. Key types of cloud migration are as follows:
Datacenter Migration
Datacenter migration is the process of transferring data from an organization’s local servers or mainframes to an external cloud solution provider, which is hosted by large, secure, and professional data centers.
The most popular method for moving datacenter resources to the cloud is through high-capacity networks; however, in situations where a strong network is not available, the resources can still be moved using high-capacity disks and “data boxes” before being actually transported to the cloud provider and uploaded to their servers.
Hybrid Cloud Migration
Many organizations use a hybrid setup to implement cloud and on-premise resources where some of them are in the cloud and others are in the datacenter. It enhances the value of the earlier established datacenter investments and helps fulfill some of the industry and compliance requirements.
This approach also brings better flexibility and scalability, where businesses can adapt the IT resources based on their needs.
Cloud-to-Cloud Migration
Organizations are increasingly using numerous cloud services for their operations, owing primarily to acquisitions. These enterprises occasionally employ cloud-to-cloud procedures to move resources from one public cloud to another.
This allows them to capture the benefits that each platform has in terms of the kind of products, services, and pricing structures it offers.
While having resources spread over different clouds may appear to be an issue, having centralized management tools allows you to monitor and regulate all cloud environments from a single console.
Application, Database, and Mainframe Migration
The most frequently performed migrations are Linux, SAP, SQL Server, and Windows Server. Companies such as IBM and Unisys frequently transfer their mainframes to the cloud.
Transferring these workloads to the cloud also brings benefits such as cost savings, improved and consolidated performance and reliability, new cloud-based developer tools and APIs, and security without the need for additional hardware capacity.
While many workloads may simply be lifted and transferred to further alter them, others can be refactored or optimized to improve their performance and resilience in the cloud.
Why Cloud Migration Matters: Key Industry Stats
- 94% of enterprises already use cloud services in some capacity, making it a proven path to innovation and efficiency. (Source: Flexera 2025 State of the Cloud Report)
- Companies experience an average of 30% reduction in IT costs within the first year of cloud migration. (Source: McKinsey & Company)
- Businesses that adopt advanced cloud migration strategies see up to 3x faster time-to-market for new products and services. (Source: Gartner)
Major Benefits of Moving to the Cloud
Organizations being more open to adopting the digital notion, and moving resources to the public cloud is a wise decision that improves business and innovation. The public cloud provides a series of benefits that can be significant in determining an organization’s performance, costs, and capabilities.
Here are some key benefits that make cloud migration an appealing choice for many businesses:
Flexibility and Scalability: Meeting Your Demands Instantly
Cloud computing offers greater flexibility and scalability than traditional IT systems, allowing businesses to adapt quickly to existing and new difficulties in the workplace.
In contrast to traditional physical IT infrastructure, where resources must be purchased and procured to meet rising demand, cloud services facilitate the use of computational resources without the need for new hardware. Whether you’re experiencing a rise in traffic or launching a new project, you can effortlessly and automatically scale up or down your resources.
Some cloud services include geographically distributed data centers, allowing you to do computations closer to your consumers, improving performance, and, as a result, customer satisfaction.
Improved Security: Safeguarding Your Data and Applications
Cloud companies are especially worried about security as they spend a lot of money protecting their platforms and their customers’ data. Platform-level security features found in public clouds include data encryption, identity and access management, and threat detection.
In other words, the cloud provider automatically fixes security flaws, simplifying the process of keeping your systems safe without requiring manual updates.
Compliance: Meeting Regulatory Standards with Ease
Cloud service providers understand the value of regulations, especially for businesses that have to go by laws and standards about privacy and data protection. Industry-specific services and certifications are now offered by the majority of cloud platforms.
This covers alternatives for data residency, security precautions, and audit tools to help with GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2 compliance.
To stay out of trouble with the law and concentrate their energies on confidently accomplishing their objectives, businesses can use cloud solutions that are compliant.
Backup, Recovery, and Failover: Ensuring Business Continuity
Cloud providers now offer backup and recovery options, as well as failovers, in order to secure your data and business operations. The built-in and one-click backup feature makes it simple for enterprises to create and store backups of their critical data in many geographic locations to avoid data loss.
If there is a data problem or a system crashes, cloud recovery technologies ensure that the systems are rapidly recovered while services remain unaffected.
Such abilities are extremely important for reducing potential risks and guaranteeing business continuity in the modern environment.
Simplified Management and Monitoring
The cloud idea expands the possibilities for resource management in data centers by providing uniform tools and monitoring. Most cloud providers offer a user-friendly shell that administrators may use to monitor and control their resources.
It simplifies the central management of an organization’s activities, such as resource allocation, performance tracking, and workload balancing. Real-time analysis of resource consumption and system state allows for the improvement of organizational processes, the optimization of IT department operations, and the attainment of overall business goals.
Cost Efficiency at Its Best
Another benefit that may entice many businesses to transfer to the cloud at any time is cost savings. Cloud providers offer management services, which reduce operational costs and make updates easier.
According to a Microsoft Office 365 survey, 82% of SMBs credit cloud computing for their decreased costs, with 70% of those savings being reinvested in the company.
Many firms can significantly lower their IT operation costs by moving to the cloud. The funds can then be utilized to invest in creative projects that promote the creation of new products and services, providing a competitive advantage and driving growth.
Innovation and Agility: Accelerating Your Competitive Edge
The cloud provides versatility by allowing developers to swiftly deploy new applications and services when the market needs them. Development teams can use a vast range of cloud-based tools and platforms to test solutions simultaneously and apply them quickly. This allows firms to compete effectively while also being better prepared to respond to changes in client wants and demands.
- Need Assistance For Your Cloud Migration?
- Get Expert Guidance and Support from Our Cloud Experts
Cloud Migration Strategies: Key Approaches for Successful Implementation
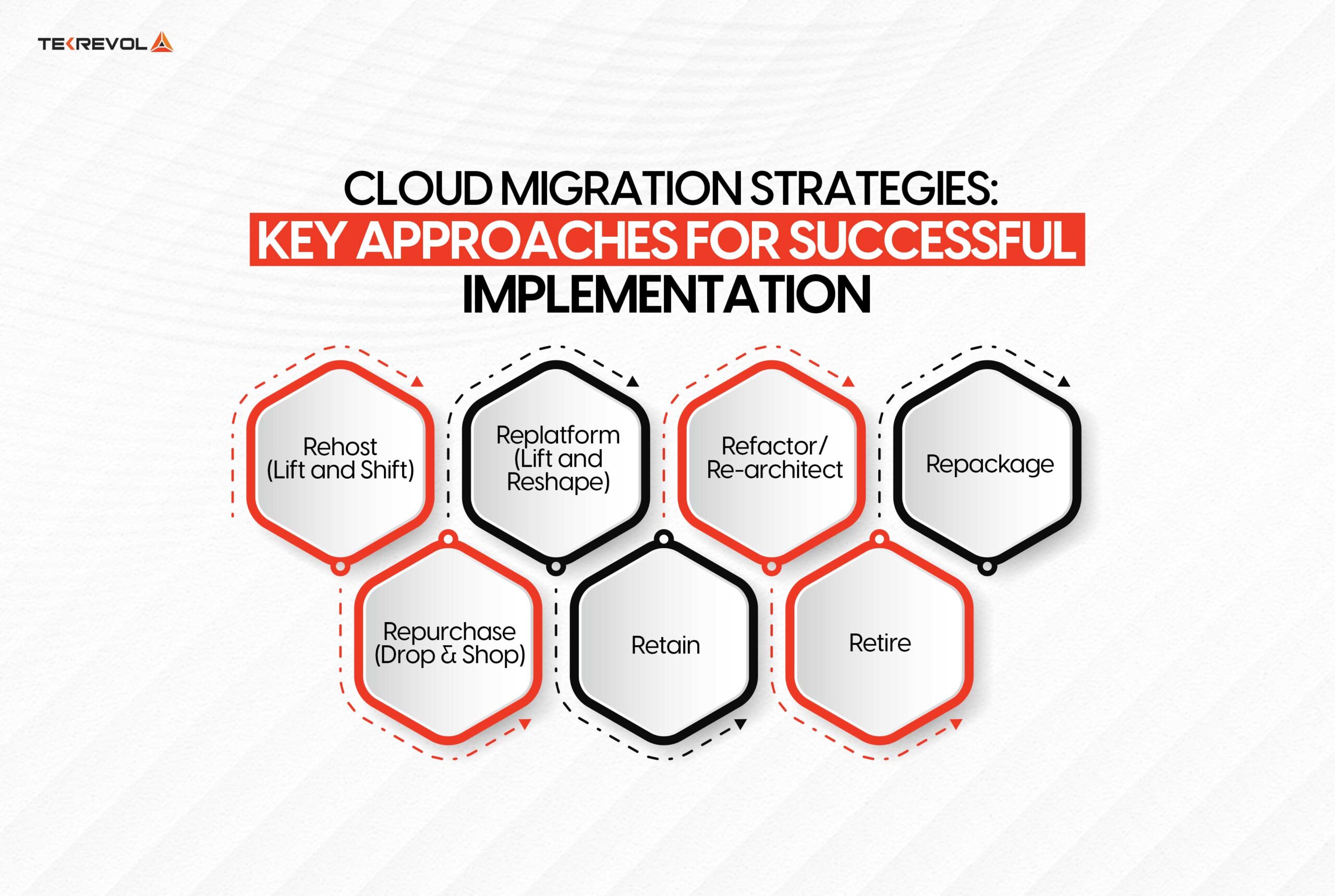
Organizations have a variety of options for organizing a cloud migration, each suited to a certain set of technical and business requirements. These tactics often referred to as the “7 Rs” offer a framework for choosing which workloads and apps should be shifted to the cloud. We’ll go over every cloud migration strategy in more detail below:
Rehost (Lift and Shift)
Rehosting refers to transferring an application from an on-premises infrastructure to the cloud with only small modifications. The primary goal is to recreate the present environment in the cloud, which is frequently accomplished through the use of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS).
This approach is quick and simple, making it appropriate for applications where structural changes are not urgently required. It enables enterprises to benefit from cloud scalability and operational savings without incurring major upfront costs for application redesign.
Replatform (Lift and Reshape)
Lift, tinker, and shift is a re-platforming strategy in which slight application optimizations are performed during migration to make use of cloud resources. This may entail altering the application architecture or components to closely resemble Platform as a Service (PaaS) solutions.
More specifically, it aims to boost efficacy, capacity, or efficiency while reducing the amount of reworking required. Replatforming is a halfway ground between speed and optimization, making it particularly appropriate for applications that require only minor improvements rather than a total redesign.
Refactor/Re-architect
Re-architecting, often known as refactoring, is the process of rewriting an application’s architecture to take full advantage of cloud-native qualities. This method aimed to improve flexibility, modularity, and efficiency by applying a variety of cloud-native solutions, including serverless computing, microservices, and containerization.
Despite the fact that refactoring is more complete and takes longer than other methods, it provides several long-term benefits like as flexibility, cost savings, and new options.
Repackage
Repackaging is the process of repackaging software in containers or virtual machines so that they can be deployed and operated on the cloud. This method focuses on improving the way deployment units are handled in an organization to increase stability.
Moving apps within a container allows for greater portability and management across various cloud and on-premise systems.
Repurchase (Drop and Shop)
Repurchasing refers to the process of replacing an old application with a new SaaS solution in a company. Companies are shifting from traditional software license models to subscription-based SaaS services provided by cloud vendors.
This method frees up the company from having to manage the infrastructure of the application, and businesses may take advantage of the dynamic changes and upgrades that SaaS providers offer. It is pertinent in situations where the SaaS services’ capabilities match the costs and business requirements.
Retain
Retention means leaving some applications or workloads in the present environment with no plans to relocate them at this time. This technique may be used when the application is a legacy system that requires considerable rebuilding to migrate to the cloud, or if the application does not justify the expense and effort of migration at this time.
Organizations may return to using these applications for migration in the future as their needs and technologies change.
Retire
Retirement is the process of stopping or decommissioning projects that are not important or relevant to the company any longer. This approach simplifies IT operations, lowers maintenance costs, and optimizes the application portfolio.
Applications may be retired as a result of obsolescence, redundancy, or a planned move to update the IT environment. A well-thought-out retirement strategy guarantees little interference with corporate operations and optimizes the use of resources for vital applications.
5 Major Cloud Migration Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Cloud migrations are complex and include certain risks. These are some of the main obstacles that businesses have while moving their resources to the cloud.
-
Lack of Planning
The absence of a well-defined strategy is one of the main barriers to cloud migration. Many firms implement cloud computing without sufficient planning, which can lead to disastrous consequences.
There is no one-size-fits-all solution; each application and dataset is distinct and has various requirements. Taking the time to create a comprehensive plan is important. Consider this: you must fully understand the commercial benefits of migrating every task to the cloud.
Every task needs a well-defined business case to ensure the migration is by your overall objectives and operational requirements. If you don’t have this, you will just make things worse for yourself later on.
-
Cost Management
To monitor spending and savings after migration, many firms neglect to set up explicit Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). Measuring the financial success of the migration is difficult because of this overlook.
Furthermore, cloud systems are dynamic, meaning that when new services are embraced and usage patterns change, costs will also change. Organizations should put strong cost management procedures in place to solve this, such as routine budgeting, optimization methods, and monitoring.
-
Vendor Lock-In
Another problem that can be linked to the use of cloud technology is vendor lock-in. Although clouds can offer a wide range of services, these are often exclusive and cannot be transferred to another cloud provider. Switching between cloud providers is not only an expensive but also a complicated procedure.
To avoid slipping into this trap, organizations need to focus on integration and think about employing several clouds. Because it can be easily modified, this technique offers more flexibility than traditional systems and lessens dependency on a particular service provider.
-
Data Security and Compliance
When moving programs and data to the cloud, security and compliance are the main issues. In order to use cloud services, an organization must secure its apps and data, while the cloud provider secures the infrastructure.
There are security hazards associated with the migration process itself. Significant exposure results from moving massive amounts of potentially sensitive data and setting up access restrictions for programs running in various contexts.
Although one of the main advantages of using cloud providers is security, it is your organization’s job to ensure that these precautions are implemented correctly and that each service or application has appropriate security measures in place.
-
Reducing Downtime for Business
Cutting down on business downtime is one of the main worries during a cloud move. If company activities are not carefully planned for, large-scale data transfers can cause significant disruptions. However, with the correct tools, they can be completed rapidly.
Some tactics to reduce downtime include using data replication techniques, thoroughly testing migration procedures beforehand, and planning migrations for off-peak times. A well-defined rollback mechanism and effective stakeholder communication can further minimize the impact of any unforeseen issues.
Cloud Migration Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
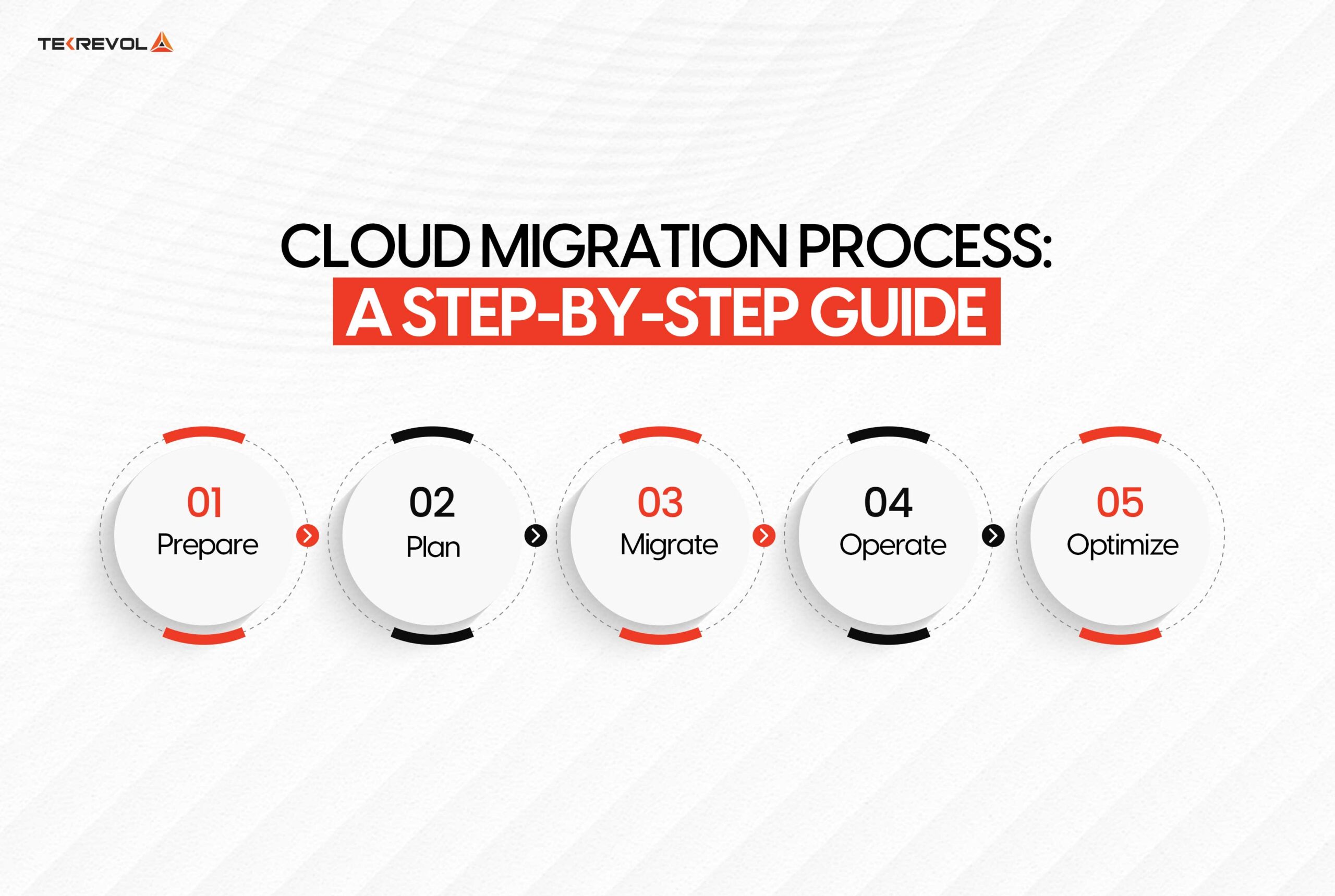
Organizations starting on a cloud migration journey go through a transformative process that involves several critical stages to assure success. To effectively carry out this process, it is essential to follow a comprehensive cloud migration checklist, as mentioned below.
1. Prepare
The transition starts with the strategy, where organizations outline their business goals for the adoption of cloud solutions. Whether one is looking at executing more flexible operations, cutting expenses, improving productivity, or expanding operations, these objectives provide the foundation for a tactical strategy
In this phase, it is significant to determine the organizational IT infrastructure’s current state and whether there are any skills or technologies that are missing.
Making a strong business case for every application that is being moved to the cloud is extremely important for ensuring an effective and economical cloud migration. This entails comparing the anticipated Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) in the cloud to the TCO presently incurred on-premises.
To precisely estimate future costs based on reasonable assumptions about storage, computing resources, instance kinds, operating systems, and particular performance and networking requirements, enterprises should use a cloud cost calculator.
2. Plan
Following preparation, the planning step tries to create a detailed migration plan. This map outlines the workload migration strategy, application selection criteria, and migration order. Another step is to successfully define the appropriate approach for cloud architecture and assess whether there are any compliance or security difficulties.
The mapping of important data demands, existing infrastructures, and compliance standards facilitates data transfer planning, which includes processes such as data cleansing and encryption.
3. Migrate
The migration phase means that you are transferring your data, applications, and workloads to the cloud at this stage. This step consists of original lift-and-shift (whereby applications are copied and adapted for the cloud), refactoring (applications are adapted for cloud features), or even rebuilding applications from scratch. Migrations must be observed closely so that if there is any hitch in the process, it is corrected early enough.
Data migration is even more important because organizations are coping with massive data volumes. If your data is not accessible during the process, it could hamper your business. While the initial migration of the system is important, maintaining the system up-to-date with the latest changes is equally important.
Any element that is moved should also be tested in the new environment before moving to the next element. Moreover, you should have a strategy on how to update it every time there is a change in the source data during migration. This helps keep everything optimized as you move to the cloud as planned.
4. Operate
Following the migration, organizations enter the operating phase, during which they manage and enhance cloud workloads, keeping an eye on multiple performance metrics, adhering to security policies, and working within budgetary constraints
Constant real-time monitoring and security assessment are necessary to guarantee that various regulatory compliances and performance standards are met.
5. Optimize
Optimization is the final stage of the cloud migration plan, and it becomes the focal point of the entire process. Organizations give considerable attention to optimizing their present and future cloud environments. This involves streamlining corporate processes, discovering cost-cutting opportunities, and utilizing built-in cloud capabilities to improve performance
Cloud optimization is a continual process in which businesses strive to improve their cloud strategies in order to maximize operational efficiency and influence business processes.
Essential Cloud Migration Tools to Streamline Your Transition
Moving apps, data, and workflows from internal data centers to cloud solutions is a difficult and time-consuming task. Cloud migration tools and services serve as facilitators, assisting in the conversion of this shift into a smooth process complete with the necessary automation capabilities.
Here are some of the best cloud migration tools and services, plus additional information to assist you make informed decisions:
1. AWS Server Migration Service (SMS)
Provider: Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Description: AWS SMS is intended to make the process of moving VMware workloads from on-premises to AWS easier. It offers tracking of the status of migrations as well as automated server discovery and replication.
Value: Organizations seeking to migrate large-scale server setups will find AWS SMS to be an effective option as it eliminates manual intervention and downtime.
2. Azure Migrate
Provider: Microsoft Azure
Description: Azure Migrate is a comprehensive package of tools and services designed to help with the assessment, planning, and implementation of migrations to Azure. AWS, other clouds, and on-premises servers are just a few of the source environments that it supports.
Value: By offering a single platform for post-migration administration and flawless integration with other Azure services, Azure Migrate ensures smoother transitions and efficient use of available resources.
3. Google Cloud Migrate
Provider: Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Description: The process of moving virtual machines (VMs) from other cloud providers or on-premises to GCP is made easier using Google Cloud Migrate. It consists of planning, execution, and assessment capabilities.
Value: Organizations may minimize risks and expenses by identifying possible problems and refining their migration strategy with the help of Google Cloud Migrate’s thorough pre-migration assessments.
4. CloudEndure Migration
Provider: CloudEndure (an AWS company)
Description: CloudEndure offers a platform-neutral solution for disaster recovery (DR) and lift-and-shift (rehost) migrations. It is compatible with multiple source settings, such as cloud-based, virtual, and physical systems.
Value: Mission-critical applications that need high availability during migration are ideally suited for CloudEndure because of its continuous replication and reduced downtime capabilities.
5. IBM Cloud Migration Factory
Provider: IBM Cloud
Description: The Cloud Migration Factory by IBM provides a number of tools and services to help with workload migrations to IBM Cloud. Phases of planning, execution, and thorough review are all included.
Value: IBM Cloud Migration Factory makes use of IBM’s vast resources and experience to offer specialized knowledge and solutions for challenging migration situations.
6. Velostrata (by Google Cloud)
Provider: Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Description: Velostrata is an expert in disaster recovery and cloud migration. It is currently a part of Google Cloud. With very little downtime, it provides real-time virtual machine streaming from on-premises to GCP.
Value: By drastically cutting down on the time and complexity of migration, Velostrata’s real-time streaming technology enables almost rapid cutovers with little to no operational disruption.
7. CloudScape (formerly Turbonomic)
Provider: CloudScape (formerly Turbonomic)
Description: CloudScape is a tool that helps businesses plan migrations and allocate resources wisely by offering workload optimization and migration features.
Value: CloudScape’s AI-powered analytics guarantee the best possible resource usage and cost-efficiency, allowing businesses to improve post-migration performance and cut expenses.
8. CloudHealth (by VMware)
Provider: VMware (now part of CloudHealth by VMware)
Description: CloudHealth provides tools for evaluating and maximizing cloud migration initiatives in addition to cloud cost management and optimization solutions.
Value: By managing and lowering cloud expenses, CloudHealth’s thorough cost analysis and optimization recommendations help enterprises maintain financial efficiency throughout the migration process.
9. RiverMeadow Cloud Migration
Provider: RiverMeadow Software
Description: RiverMeadow provides cloud-based workloads—physical, virtual, and cloud—with automated server migration solutions across many cloud platforms.
Value: RiverMeadow offers a scalable and affordable solution for companies of all kinds, catering to a wide range of migration requirements because of its end-to-end automation and adaptability.
10. Cloud Vendors’ Migration Services
Providers: AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, IBM Cloud, and others
Description: All major cloud providers offer migration services and tools. For example, AWS has the AWS Database Migration Service (DMS), but Azure has Azure Site Recovery, which is primarily intended for disaster recovery and migration.
Value: Cloud providers offer native migration services that are compatible and give help for the migration process as well as extra cloud services.
Tips to Choose the Right Tools and Services
When planning a cloud migration, it’s significant to:
- Assess Specific Needs: Try to discover the needs of your specific organization such as the type of workloads as well as compliance and migration requirements.
- Evaluate Available Tools: Select the tools and services that provide as many features and capabilities as possible and are affordable for your migration plan.
- Consider Third-Party Support: Various consulting firms and managed service providers offer specific migration services that might offer further value.
If organizations are keen on choosing the right tools and services, they can reduce risks associated with cloud migration, while at the same time, maximizing the benefits that are associated with cloud migration.
How Does TekRevol Help You With Cloud Migrations?
TekRevol has extensive experience assisting organizations in migrating to the cloud, offering a variety of cloud consulting services designed to ensure a smooth transition.
Our team’s professional cloud migration plan begins with an evaluation of your current IT environment and organizational goals, followed by the development of a migration plan customized to your company’s specific needs.
From offering cloud migration strategies to help businesses manage their cloud infrastructure, TekRevol provides comprehensive cloud managed services, ongoing optimization, and support to ensure flawless cloud operations and maximize your cloud investment.
We manage every phase of cloud migration, from planning and implementation to ongoing support and optimization. This ensures that your cloud environment operates smoothly and affordably after migration, allowing your business to fully benefit from cloud computing.
- Want to Experience Hassle-Free Cloud Migration ?
- Our cloud Experts Help You Plan, Execute, and Optimize Your Migration








![How to Monetize a Game [2026 Strategies & Models]](https://d3r5yd0374231.cloudfront.net/images-tek/uploads/2026/01/Tek-Feature-3.jpg)



